2:17 PM Introduction to DHCP ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) | Rahul Tyagi White Hat Blog | |
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol-based client / server architecture that is used to facilitate the allocation of IP addresses in one network. A local network that does not use DHCP to give IP addresses to all computers manually.
If DHCP is installed on the local network, all computers are connected
in a network will get an IP address automatically from a DHCP server. In addition to IP addresses, many network parameters that can be provided by the DHCP, such as default gateway and DNS server.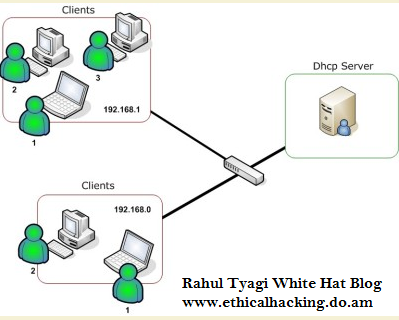 Since DHCP is a protocol that uses client / server architecture, then the DHCP there are two parties involved, namely DHCP Server and DHCP Client. * DHCP server is a machine that runs a service that can be "leased" IP addresses and TCP / IP information to all other clients who request it. Some network operating systems like Windows NT Server, Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003, or GNU / Linux have this service. * DHCP client is a client machine running the DHCP client software that allows them to be able to communicate with the DHCP Server. Most network client operating systems (Windows NT Workstation, Windows 2000 Professional, Windows XP, Windows Vista, or GNU / Linux) have a software like this. DHCP servers generally have a set of addresses that are allowed to be distributed to clients, referred to as DHCP Pool. Each client would then hire an IP address from the DHCP pool is for the time specified by the DHCP, usually up to several days. When the IP address lease time expires, the client will ask the server to provide new IP address or extend it. DHCP Client will try to get the "leasing" an IP address from a DHCP server in the following four steps: 1. DHCPDISCOVER: DHCP client will deploy a broadcast request to locate a DHCP server is active. 2. DHCPOFFER: Having heard the broadcasts from the DHCP Server DHCP Client, DHCP server then offers an address to the DHCP client. 3. DHCPREQUEST: Client request DCHP server to lease IP addresses from one of the available addresses in the DHCP pool on the DHCP server in question. 4. DHCPACK: DHCP server will respond to requests from the client by sending an acknowledgment packet. Then, the DHCP server will assign an address (and configuration of TCP / IP) to the client, and update database data bases his. The client will then begin the process of binding the protocol stack TCP / IP and therefore already has an IP address, the client can initiate communication. The concept of serving DHCP requests from the clientnya, ask for the IP to be automatically propagated to client2. > DHCP is designed to serve a large network and TCP / IP configuration of complex .... This applies if the computer is using IP settings with DHCP or in Windows to enable the option "Obtain IP Address Automatically" I know my purpose .. Then if there is a DHCP server with IP range 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.10.200, then any computer connected to the network and enable the use of DHCP, the DHCP server will assign IP addresses in the range above that is between 100 - 200. On the network if there is a computer with a Static IP and IP are still in the range of the DHCP Server DHCP Server will not use that IP to be given to other DHCP users .. * IP Address mean = network address = Host address PROCESS DHCP: 1. Identify the DHCP Server 2. Requesting an IP 3. Receive IP 4. Deciding To Use IP DHCP uses the concept of the DHCP relay agent (not henti2) disconnected continue despite death, the DHCP relay agent is a host who continues the DHCP packets between Client and server. Relay agents are used to continue the request and replies between the client and the server that they are not in the same physical subnet ... Configuring DHCP DHCP server database is organized like a tree. The root of the tree is the address pool for natural networks, branches dalah subnetwork address pools, and leaves manually bind the client. Subnetworks inherit network parameters and clients inherit subnetwork parameters. Therefore, most of the parameters, such as domain names, need to be configured at the highest level. DHCP Weaknesses These weaknesses include interlinked computers DHCP unwanted entry on computer networks. So the computer or laptop that is unwanted can access resources on the network.So if there is no MAC address is not listed in the DHCP server computer, then the computer can not access the network. | |
|
| |
Wednesday, 2025-07-16, 1:05 AM
|
Main » 2012 January 8 » Introduction to DHCP ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) | Rahul Tyagi White Hat Blog
|


